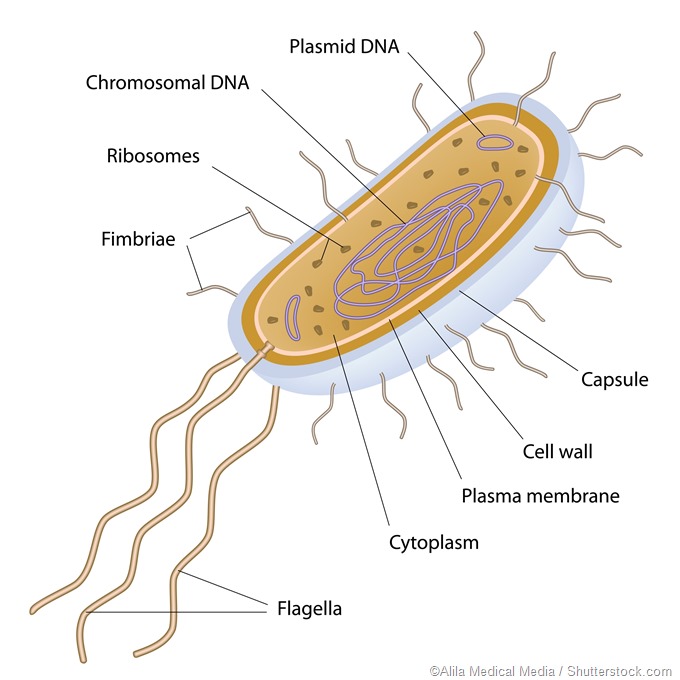
Can Goji berry kill cervical cancer Biology Diagrams The prokaryotic cells have four main components: Plasma Membrane- It is an outer protective covering of phospholipid molecules which separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Cytoplasm- It is a jelly-like substance present inside the cell.All the cell organelles are suspended in it. DNA- It is the genetic material of the cell.All the prokaryotes possess a circular DNA.
Typically, prokaryotic cell sizes range from 0.1 to 5.0 μm in diameter and thus are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells. They have a surface area to volume ratio higher than eukaryotes because of their small size. Shapes. The three most common prokaryotic cell shapes are spiral (coiled-shaped), bacillus (rod-shaped), and coccus The Components of a Typical Prokaryotic Cell. All prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleoid, and ribosomes. Other components vary by species. Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance inside the cell that surrounds all other cell components, like ribosomes and DNA. The cytoplasm is primarily water but also includes

15.1: The Prokaryotic Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram. The following image is a diagram of a prokaryotic cell; in this case, a bacterium. The Anatomy of a Bacterial Cell Prokaryotic Cell Structure. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do.

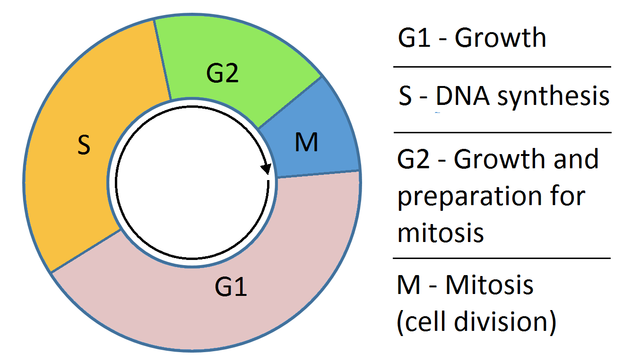
What is the cell cycle. Its stages are described in order along with the parts, regulation, life cycle & purpose. Cell Cycle Diagram. Phases of the Cell Cycle single-celled (prokaryotes) organisms than higher multicellular (eukaryotes) ones. The reason is that a prokaryotic cell has a relatively simpler cell organization with a single

Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, and Diagram Biology Diagrams
Structure of Prokaryotic Cells. The diagram of prokaryotic cells shows that it has a simple structure and lack complex organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. The prokaryotic cells example are archae and bacteria. The structure of a prokaryotic cell is discussed below: Size of prokaryotic cells can vary betwween 0.1 -5.0 µm. The following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. The phases are: 1. G 1 (gap1) phase 2. S (synthesis) phase 3. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. M (mitosis) phase. Cell Cycle: Phase # 1. G 1 Phase: . The G 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic state to the more extended interphase state and The G 0 phase is a "resting" phase where the cell exits the cell cycle and stops dividing. Some cells, like neurons and muscle cells, enter this phase semi-permanently and may never undergo division again. This phase is crucial for: Conserving energy and resources in non-dividing cells. Specializing cells for specific functions. Regulation